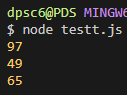
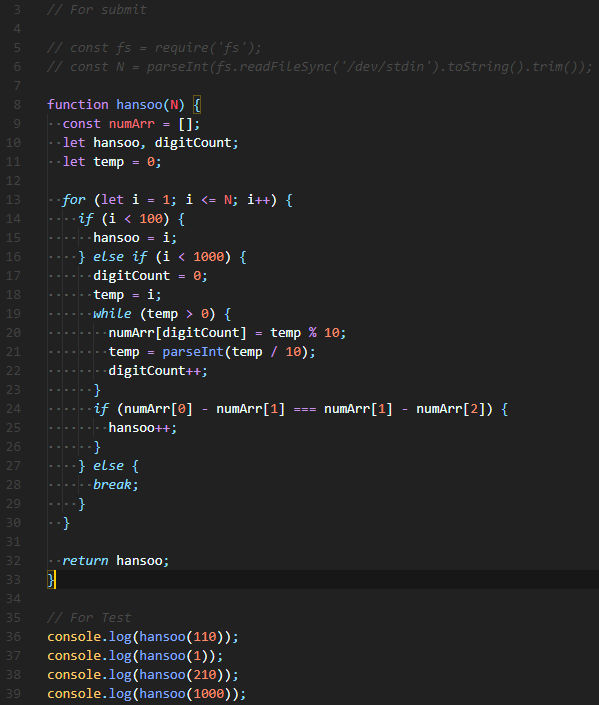
Q. 정수 n을 입력받아, Fibonacci(피보나치 수열)의 n번째 수를 출력하라.
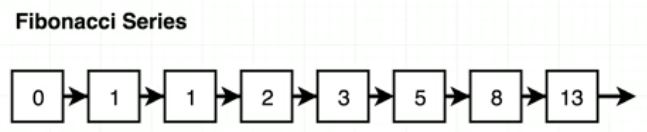
피보나치 수열이란 처음 두 항을 1과 1로 한 후, 그 다음 항부터는 바로 앞의 두 개의 항을 더해 만드는수열을 말한다.
For example, the sequence
[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
forms the first ten entries of the fibonacci series.
Example:
fib(4) === 3
Code
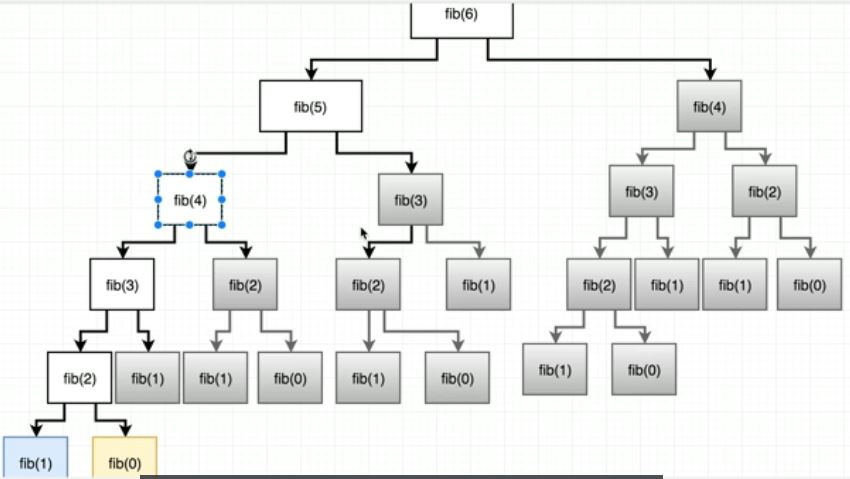
😢 배열을 이용한 단순 fib는 쉽게 풀었고, recursion(재귀)를 사용하는 fib는 생각하기에는 어려웠지만 단순했고, memoize(Dynamic Programming)은 매우 생소해서 익숙해지는 시간이 필요했다.
😊 Solution 1)
index 0과 1의 값을 미리 저장한 배열(array)를 선언해주고, classic for loop을 반복해주었다.
i는 1부터 시작해주고 arr.push(arr[i-1] + arr[i-2])형식으로 index를 조정해주어 값을 push해주고 arr[n]을 출력해주면 된다.
Solution 2) 재귀함수(Recursion)
재귀함수를 이용한다.
만약 n값이 2보다 작다면 n값을 return하는 Base Case를 걸어두어 간단하게 해결할 수 있다.
(무조건 index 0은 0이고, index 1은 1로 시작하기 때문이며, 최대 -2를 해주므로, 0또는 1값만 발생할 수 있다)
0, 1, 1이 합쳐져 다음 수를 만들고, 이것들이 결과적으로 피보나치 수열을 이루기 때문이다(결국 1을 찾는 것이다)
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);을 통해 처음부터 끝까지 모든 경우의 수를 재귀적으로 실행한다.

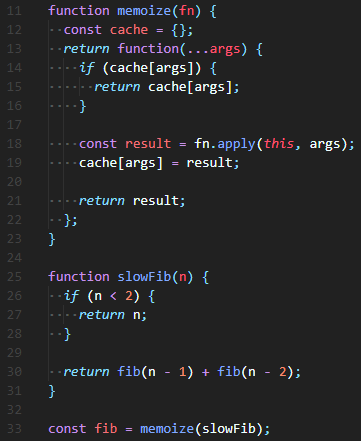
Solution 3) 재귀함수와 Memoize(Dynamic Programing)
재귀함수로 검색을 해주지만, 모든 경우의 수를 탐색하지 않고, cache를 생성하여 한 번 검색한 값은 저장하고, 다시 탐색하지 않는다.
재귀함수 fib(여기서는 slowFib)를 memoize함수 안에서 실행하도록 하여, 한 번 탐색한 값은 cache object에 저장하고 그 값을 다시 탐색한다면 cache에서 값을 꺼내 반환해준다. 만약 처음으로 탐색하는 값이라면 slowFib를 실행시킨다.
이렇게 재귀함수를 사용해주면 시간낭비 없이 효율적으로 재귀를 진행할 수 있다.
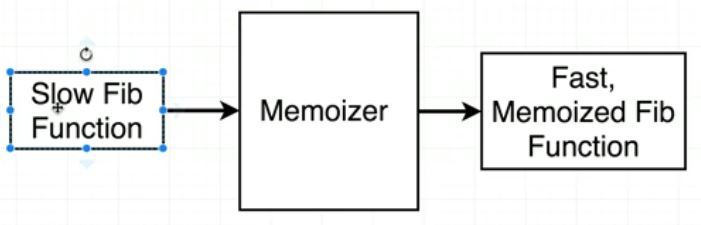
✔ Nested functions
Memoize function안에 inner function을 만들어줘서, 이미 검색한 값이라면 cache[args]를 리턴, 그게 아니라면 검색하게 한다.
이 과정을 통해 시간 복잡도를 줄일 수 있다. 검색하는 시간을 줄여주기 때문이다.
JavaScript - Grammar 카테고리에서 조금 더 다뤄 보겠다.
✔ Function.prototype.apply()
memoize의 inner function에서 slowFib를 실행시켜주는 방법이다.
helper method 카테고리에서 조금 더 다뤄 보겠다.
✔ this
이 문제에서는 사실 apply()의 첫 번째 parameter에 null or this를 넣어도 큰 상관은 없지만, this로 넣어줬다.
간단히 말하자면 this는 자신의 왼쪽(소속)을 나타낸다.
JavaScript - Grammar에서 조금 더 다뤄 보겠다.
✔ args(The arguments object)
입력값을 간접적으로(?) 넘겨주기 위해 사용했다.
function안에서 다룰 수 있는 Array-like object인 arguments이며,
JavaScript - Grammar에서 조금 더 다뤄 보겠다.
✔ ... (Spread)
args를 array처럼 만들어 줄 수 있다. apply()의 두 번째 parameter가 array이므로 array-like값을 넘어주기 위해 사용했다.
JavaScript - ES2015 카테고리에서 개념을 확인할 수 있다.
Full Code
| function memoize(fn) { |
| const cache = {}; |
| return function(...args) { |
| if (cache[args]) { |
| return cache[args]; |
| } |
| const result = fn.apply(this, args); |
| cache[args] = result; |
| return result; |
| }; |
| } |
| function slowFib(n) { |
| if (n < 2) { |
| return n; |
| } |
| return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2); |
| } |
| const fib = memoize(slowFib); |
| // function fib(n) { |
| // const result = [0, 1]; |
| // for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) { |
| // const a = result[i - 2]; // === result[result.length -2]; |
| // const b = result[i - 1]; // === result[result.length -1]; |
| // result.push(a + b); |
| // } |
| // return result[n]; // === result[result.length -1]; |
| // } |
| // function fib(n) { |
| // if (n < 2) { |
| // return n; |
| // } |
| // return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2); |
| // } |
'Algorithm > JavaScript(Node.js)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 10809번: 알파벳 찾기(Find alphabet) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.01 |
|---|---|
| 백준 11720번: 숫자의 합(The sum of numbers) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.01 |
| Spiral Matrix(나선형 행렬 - 달팽이) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.01 |
| Vowels(모음 찾기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.31 |
| Pyramid(피라미드 출력하기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.31 |