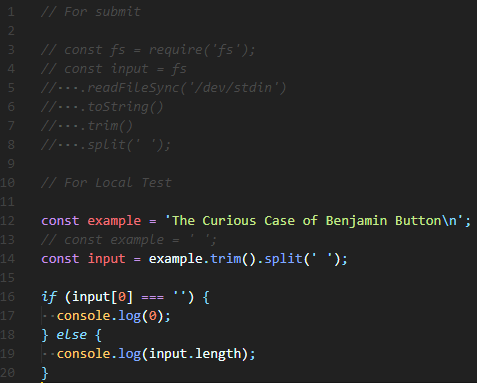
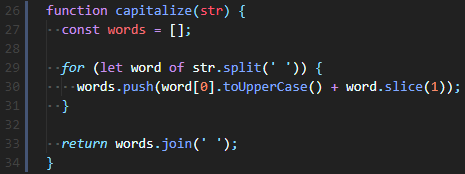
Q. 입력받은 n(숫자)만큼의 층을 생성하는 피라미드를 출력하라.
(단, n은 양수이며, 각 층의 양측 공백은 space로 채워야한다)
--- Examples
pyramid(1)
'#'
pyramid(2)
' # '
'###'
pyramid(3)
' # '
' ### '
'#####'
Code
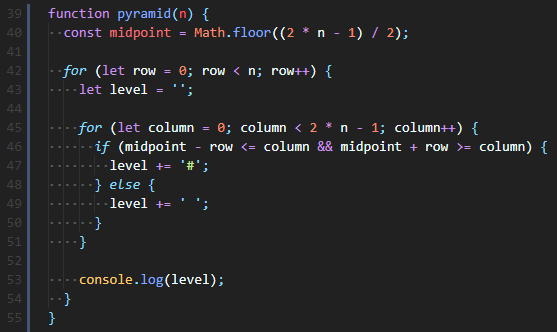
😢 각 층(level)의 column은 홀수로 출력되어야 하며, 가운데(midpoint)를 찾아 확장하는 것이 핵심이다.
이 두 가지 핵심 포인트를 찾는 것에 시간이 조금 걸렸다.

😊 Solution 1)
먼저, 해당 피라미드의 가운데지점(midpoint)을 세팅해준다. (2*n-1)
외부 for loop의 row(행)은 각 층수이기 때문에 받은 숫자(n)만큼 반복되고,
내부 for loop의 column(열)은 항상 홀수로 출력되어야 하기 때문에 2*n-1만큼 반복되어야 한다.
그리고 만약 각 층의 #이 채워질 범위가 midpoint - row <= column <= midpoint + row에 해당하면 #,
그게 아니라면 ' '(space)를 level에 대입해준다. 그리고 내부 for loop이 끝날 때마다 각 층을 출력해준다.
Solution 2) 재귀함수
먼저, 함수의 parameter에 row=0, level='' 을 default로 설정해준다. 초기화 후 다른 값으로 반복 대입이 필요하기 때문이다.
Base Case 1)로 만약 row(행)가 n(받은 입력값)과 같으면 return;하여 작업을 끝내주고,
Base Case 2)로 만약 각 층의 값이 level.length(2*n-1)만큼 채워지면 다음 row(층) 작업(재귀)을 실행시켜주고,
원래 하던 작업은 return; 시켜준다.(중요)(Solution 1의 column을 여기서는 level로 대체해준다)
만약 return해주지 않으면, 아래로 작업이 진행되기 때문에 의도하지 않는 실행이 발생될 수 있기 때문이다.
그 후 Solution 1)과 마찬가지로 midpoint - row <= level.length <= midpoint + row 범위에 해당하면 #,
그게 아니라면 ' '을 level에 대입하여준다.
그리고 각 층의 level.length만큼 반복시켜주기 위해 pyramid(n, row, level + add)로 각 층을 재귀함수로 반복시켜준다.
✔ default
function pyramid(n, row=0, level='') 좌측의 row와 level은 입력받지 않는 이상 default인 0과 ''로 실행된다.
https://babeljs.io/docs/en/learn/#default-rest-spread
Babel · The compiler for next generation JavaScript
The compiler for next generation JavaScript
babeljs.io
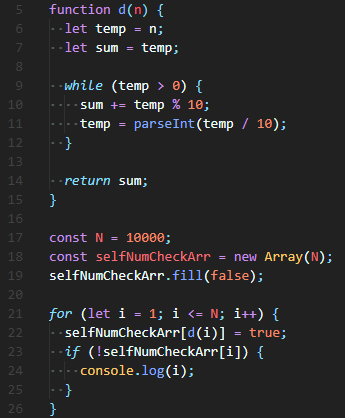
Full Code
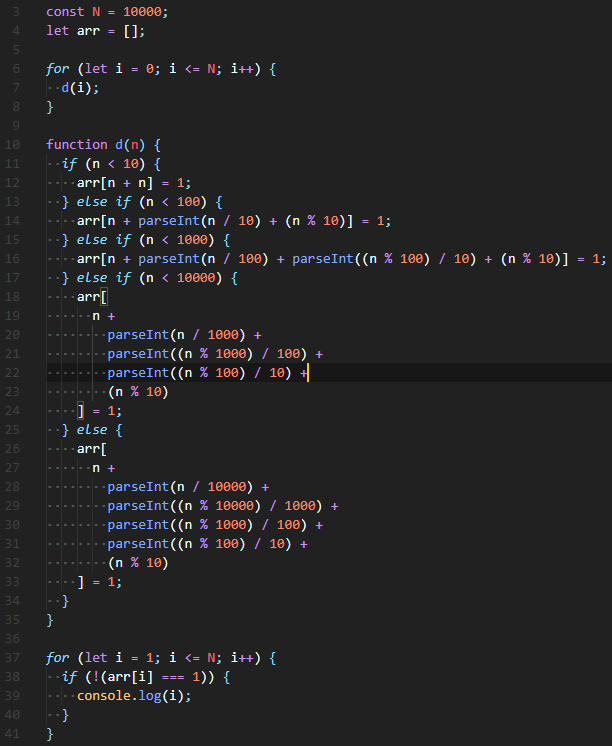
| function pyramid(n, row = 0, level = '') { |
| if (row === n) { |
| return; |
| } |
| if (level.length === 2 * n - 1) { |
| console.log(level); |
| return pyramid(n, row + 1); |
| } |
| const midpoint = Math.floor((2 * n - 1) / 2); |
| let add; |
| if (midpoint - row <= level.length && midpoint + row >= level.length) { |
| add = '#'; |
| } else { |
| add = ' '; |
| } |
| pyramid(n, row, level + add); |
| } |
| // function pyramid(n) { |
| // const midpoint = Math.floor((2 * n - 1) / 2); |
| // for (let row = 0; row < n; row++) { |
| // let level = ''; |
| // for (let column = 0; column < 2 * n - 1; column++) { |
| // if (midpoint - row <= column && midpoint + row >= column) { |
| // level += '#'; |
| // } else { |
| // level += ' '; |
| // } |
| // } |
| // console.log(level); |
| // } |
| // } |
'Algorithm > JavaScript(Node.js)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spiral Matrix(나선형 행렬 - 달팽이) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.01 |
|---|---|
| Vowels(모음 찾기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.31 |
| 백준 11654번: 아스키 코드(ASCII Code) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.31 |
| 백준 1152번: 단어의 개수(The number of words) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.31 |
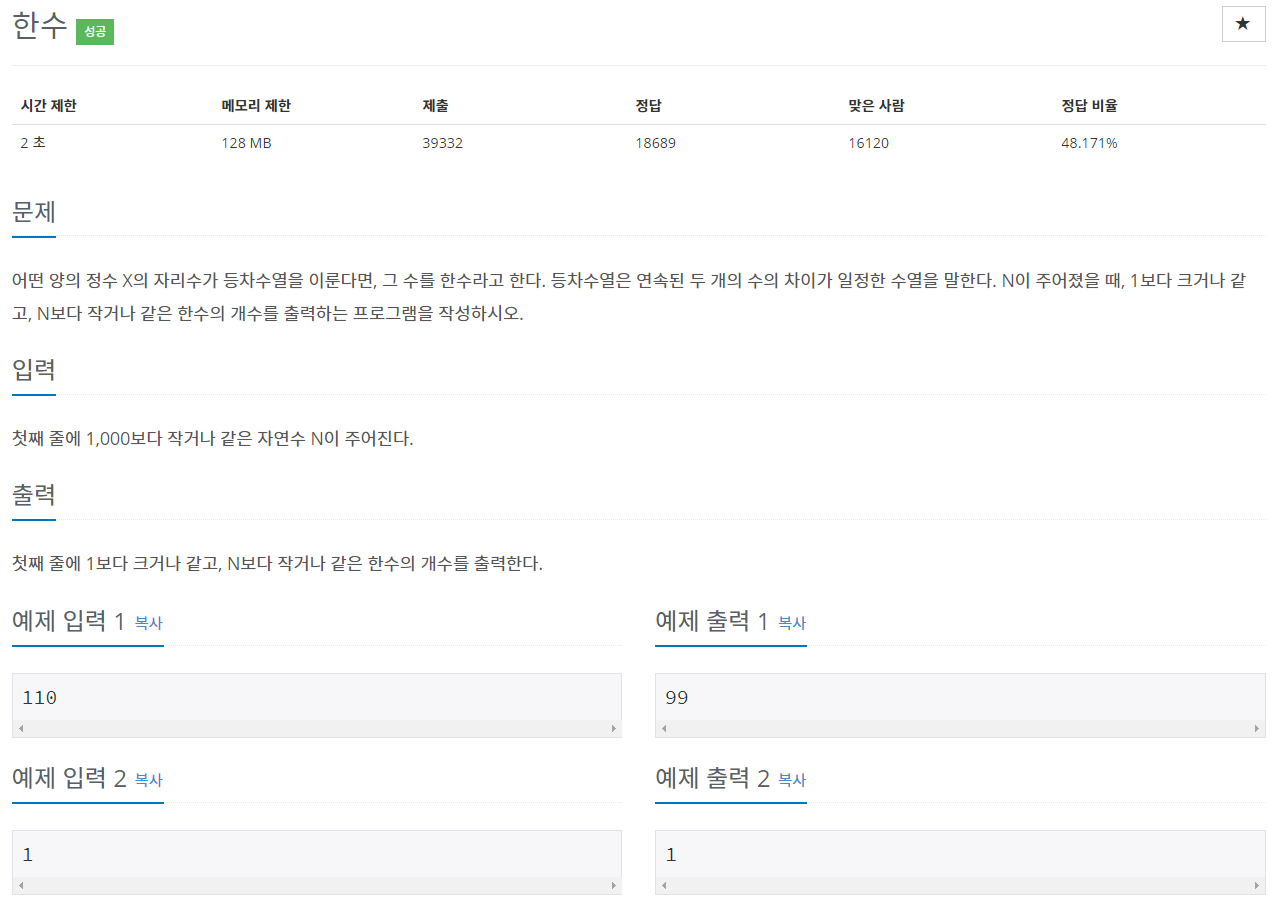
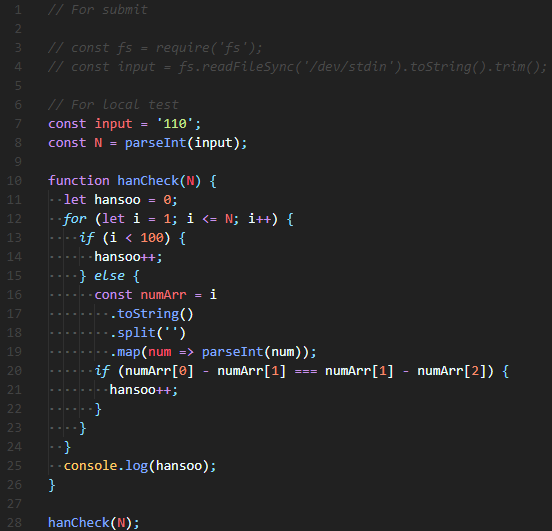
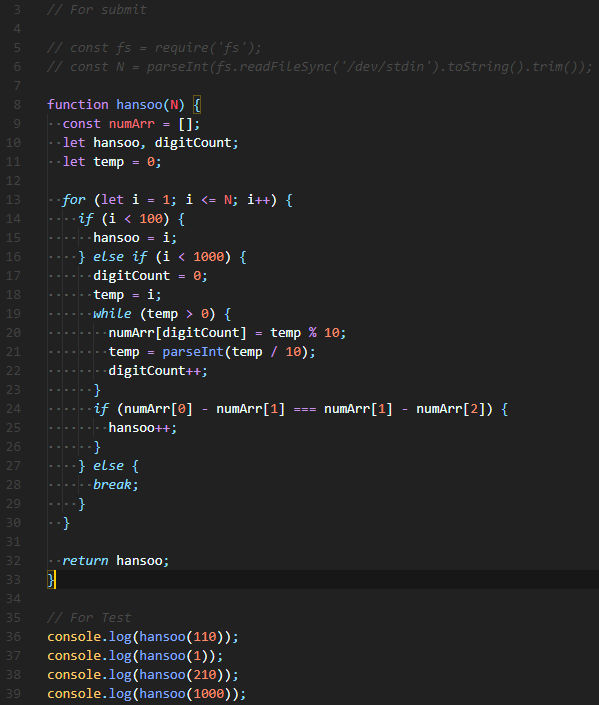
| 백준 1065번: 한수(an arithmetical progression) Node.js(JavaScript) [수정 및 추가] (0) | 2019.12.30 |