Code
😢 21억 조건을 못 보고 반복문을 돌려 counter를 하나씩 증가시키려고 했다.. 잘못된 방법!
😊 역시나 수학 카테고리답게 다항식을 이용해서 풀면 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
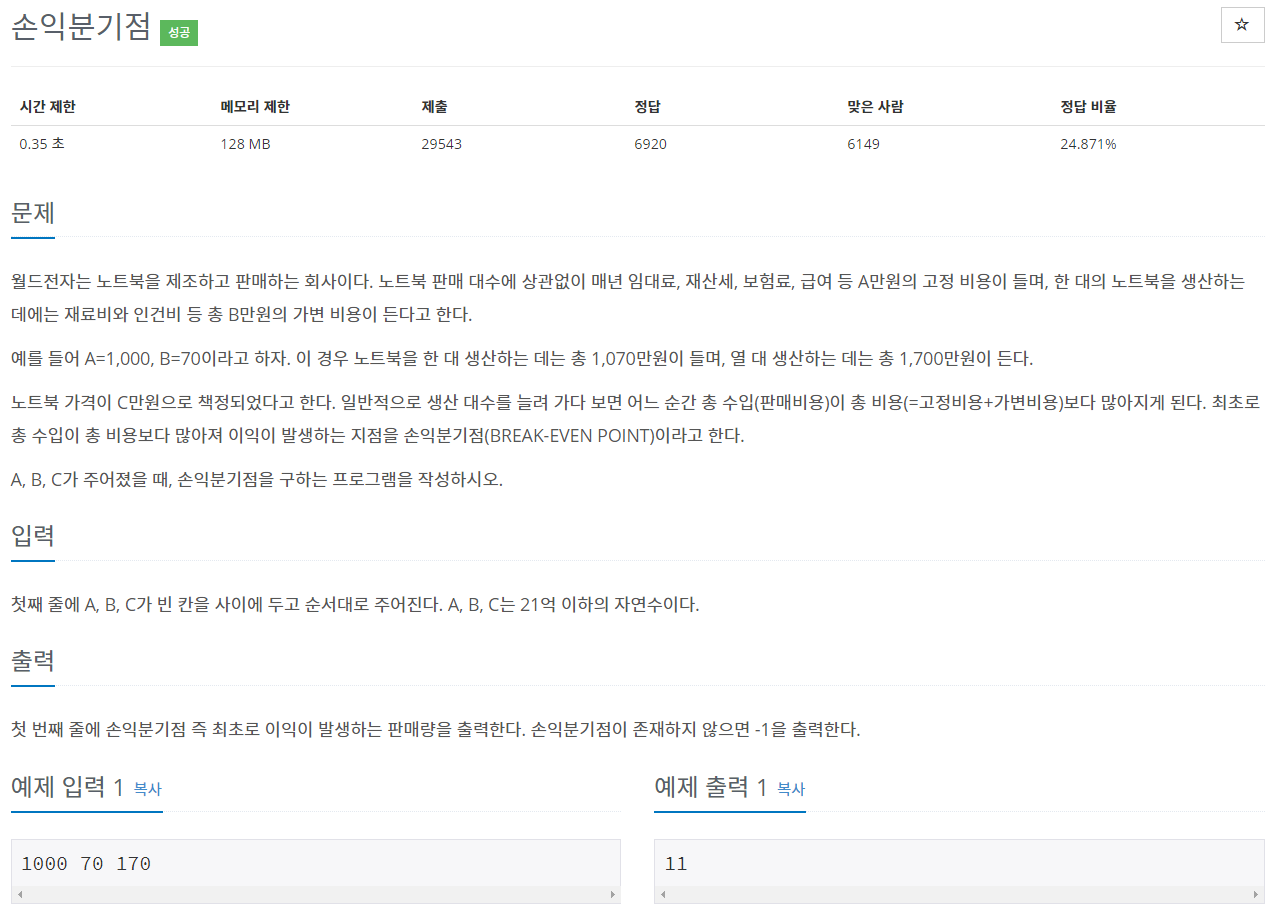
A는 고정 비용, B는 가변 비용, C는 판매 가격이다.
판매 누적 금액이 고정비용+가변 누적 비용을 넘어서면 손익분기점을 넘어간다.
식을 만들어 본다면, A + Bx < Cx로 만들 수 있다.
식을 정리해보자. A < Cx - Bx로 Bx를 넘겨주고, A < (C-B)x 로 정리해주면 조금 더 보기 쉽다.
즉, C-B가 0이하(즉, 0 또는 음수)로 떨어지면 손익분기점은 없다. 계속 적자다..ㅎㅎ
손익분기점이 없어서 '-1'을 출력하는 조건문은 2가지 정도로 표현할 수 있다.
1. if(C-B <= 0) { console.log(-1); }
A < (C-B)x 식을 생각해서 C-B가 0이하면 손익분기점은 없다고 표현할 수 있다.
2. if(C <= B) { console.log(-1); }
C-B > 0이 돼야하므로, C <= B으로 정리해주면 손익분기점이 없다고 표현할 수 있다.
Full Code
| // Break-Even Point |
| // 1st Solution(other) |
| // For submit |
| // const fs = require('fs'); |
| // const input = fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim().split(' '); |
| // For local test |
| const input = ['1000', '70', '170']; |
| const A = parseInt(input.shift()); |
| const B = parseInt(input.shift()); |
| const C = parseInt(input.shift()); |
| const netProfit = C - B; |
| if (netProfit <= 0) { |
| console.log(-1); |
| } else { |
| console.log(Math.floor(A / netProfit) + 1); |
| } |
| // 2nd Solution(ohter) |
| // For submit |
| // const fs = require('fs'); |
| // const input = fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim().split(' ').map(num => parseInt(num)); |
| // For local test |
| // const input = ['1000', '70', '170'].map(num => parseInt(num)); |
| // const A = input.shift(); |
| // const B = input.shift(); |
| // const C = input.shift(); |
| // if (C <= B) { |
| // console.log(-1); |
| // } else { |
| // console.log(Math.floor(A / (C - B)) + 1); |
| // } |
'Algorithm > JavaScript(Node.js)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2292번: 벌집(Honey Comb) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.13 |
|---|---|
| 백준 2839번: 설탕 배달(Sugar Delivery) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.11 |
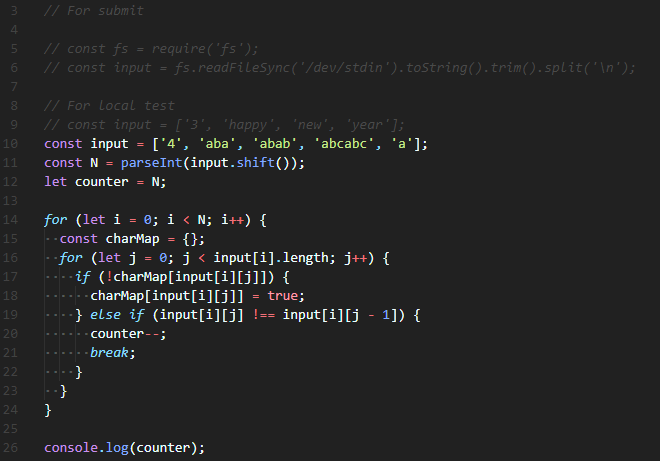
| 백준 1316번: 그룹 단어 체커(Group Word Checker) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.09 |
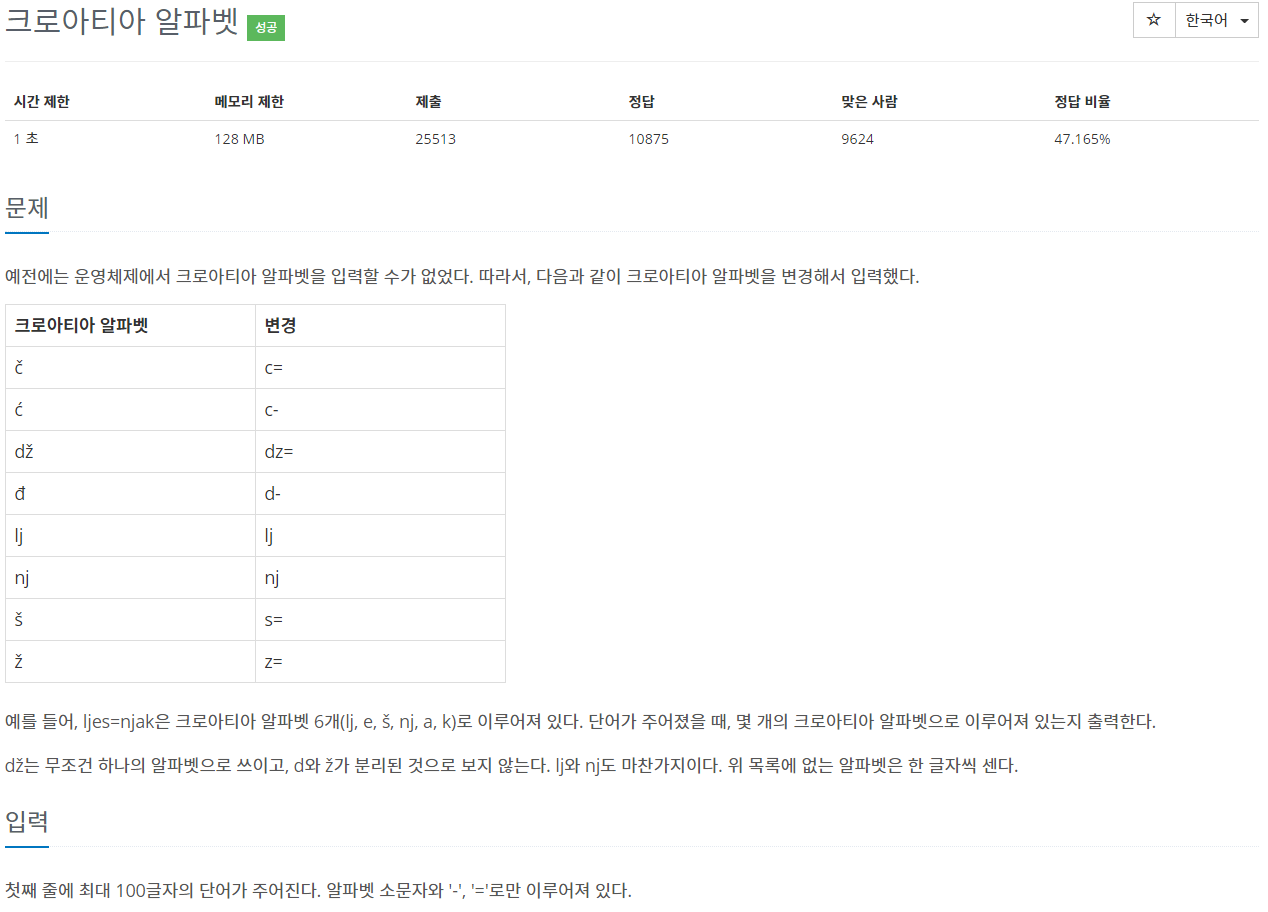
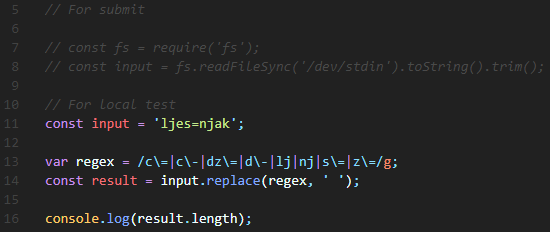
| 백준 2941번: 크로아티아 알바펫(Croatia Alphabet) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.06 |
| 백준 5622번: 다이얼(Dial) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2020.01.06 |