Code
😢 5분 정도 고민하고, 코드로 하나씩 정리해 나가면서 금방 풀 수 있었던 문제
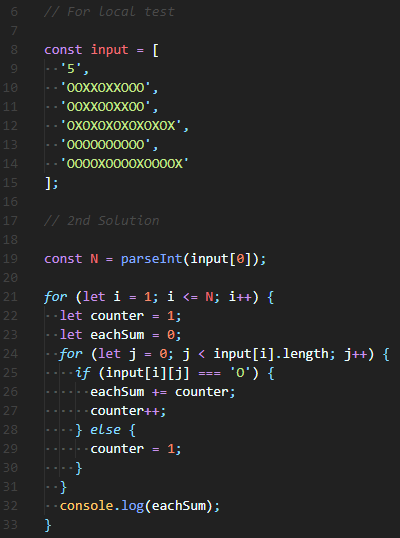
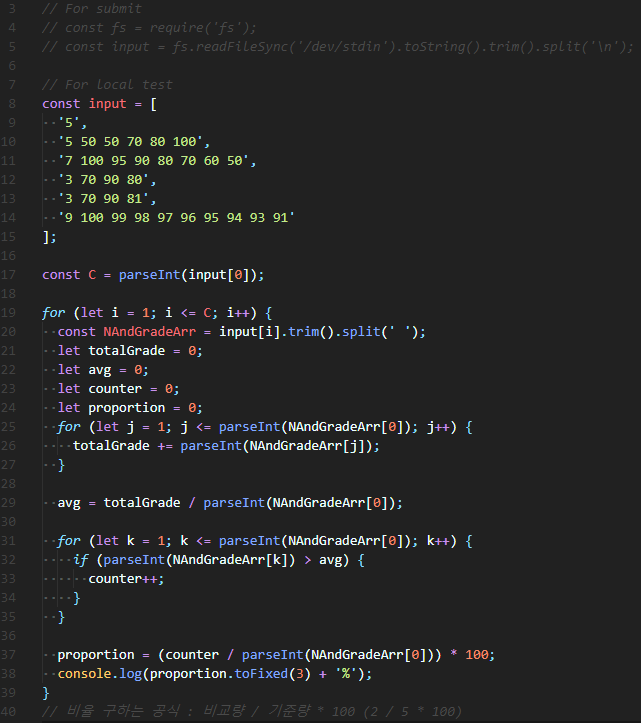
😊 전체 Test Case를 반복할 수 있는 for loop을 가장 바깥에서 돌리고, 중첩 첫 번째 for loop에서 점수를 모두 더해준 후 평균을 구한다. 그리고 중첩 두 번째 for loop에서 평균보다 높은 인원수를 구하고 비율을 계산해주고 출력한다.
평균을 어떻게 구할지, 평균을 넘는 인원은 몇명인지, 비율을 구하는 공식은 무엇인지 먼저 정리하고 풀어나가면 금방 해결할 수 있다.
Full Code
| // 1st Solution |
| // For submit |
| // const fs = require('fs'); |
| // const input = fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim().split('\n'); |
| // For local test |
| const input = [ |
| '5', |
| '5 50 50 70 80 100', |
| '7 100 95 90 80 70 60 50', |
| '3 70 90 80', |
| '3 70 90 81', |
| '9 100 99 98 97 96 95 94 93 91' |
| ]; |
| const C = parseInt(input[0]); |
| for (let i = 1; i <= C; i++) { |
| const NAndGradeArr = input[i].trim().split(' '); |
| let totalGrade = 0; |
| let avg = 0; |
| let counter = 0; |
| let proportion = 0; |
| for (let j = 1; j <= parseInt(NAndGradeArr[0]); j++) { |
| totalGrade += parseInt(NAndGradeArr[j]); |
| } |
| avg = totalGrade / parseInt(NAndGradeArr[0]); |
| for (let k = 1; k <= parseInt(NAndGradeArr[0]); k++) { |
| if (parseInt(NAndGradeArr[k]) > avg) { |
| counter++; |
| } |
| } |
| proportion = (counter / parseInt(NAndGradeArr[0])) * 100; |
| console.log(proportion.toFixed(3) + '%'); |
| } |
| // 비율 구하는 공식 : 비교량 / 기준량 * 100 (2 / 5 * 100) |
| // other solution (좀 특이해서 참고해보았다) |
| // var a = require('fs') |
| // .readFileSync('/dev/stdin') |
| // .toString() |
| // .match(/[^\r\n]+/g) |
| // .slice(1), |
| // b = a.map(function(x) { |
| // return x.split(' '); |
| // }), |
| // c = [], |
| // e = []; |
| // for (var i = 0; i <= b.length - 1; i++) { |
| // c.push( |
| // b[i].reduce(function(pre, cur) { |
| // return parseInt(pre) + parseInt(cur); |
| // }) / |
| // b[i][0] - |
| // 1 |
| // ); |
| // e.push( |
| // b[i].slice(1).filter(function(x) { |
| // return x > c[i]; |
| // }) |
| // ); |
| // console.log(((e[i].length / b[i][0]) * 100).toFixed(3) + '%'); |
| // } |
'Algorithm > JavaScript(Node.js)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 4673번: 셀프 넘버(Self Number) Node.js(JavaScript) [수정 및추가] (0) | 2019.12.29 |
|---|---|
| Chunk(size만큼 sub array 잘라 넣기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.29 |
| Anagrams(철자 순서를 바꾼 말) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.28 |
| 백준 8958번: OX 퀴즈(OX Quiz) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.27 |
| The Classic FizzBuzz(3의 배수와 5의 배수 찾기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.27 |