'Algorithm > C&C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2576번: 홀수(c/c++, c/cpp) (0) | 2021.10.05 |
|---|---|
| 백준 2562번: 최댓값(c/c++, c/cpp) (0) | 2021.10.05 |
| 백준 2480번: 주사위 세개(c/c++, c/cpp) (0) | 2021.09.29 |
| 백준 2753번: 윤년(c++) (0) | 2021.09.29 |
| 백준 1000번: A+B(c++) (0) | 2021.09.27 |

| 백준 2576번: 홀수(c/c++, c/cpp) (0) | 2021.10.05 |
|---|---|
| 백준 2562번: 최댓값(c/c++, c/cpp) (0) | 2021.10.05 |
| 백준 2480번: 주사위 세개(c/c++, c/cpp) (0) | 2021.09.29 |
| 백준 2753번: 윤년(c++) (0) | 2021.09.29 |
| 백준 1000번: A+B(c++) (0) | 2021.09.27 |

| 백준 2480번: 주사위 세개(c/c++, c/cpp) (0) | 2021.09.29 |
|---|---|
| 백준 2753번: 윤년(c++) (0) | 2021.09.29 |
| 백준 2752번: 세수정렬 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 백준 10871번: X보다 작은 수 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 백준 10804번: 카드 역배치 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.02 |

😢 단순 비교도 가능하지만, 정렬로 쉽게 풀 수 있는 문제
😊 각종 정렬을 이용해 풀 수 있음(여기선 선택정렬 selection sort)
| 백준 2753번: 윤년(c++) (0) | 2021.09.29 |
|---|---|
| 백준 1000번: A+B(c++) (0) | 2021.09.27 |
| 백준 10871번: X보다 작은 수 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 백준 10804번: 카드 역배치 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.02 |
| 백준 2440번: 별 찍기 - 3 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.01 |
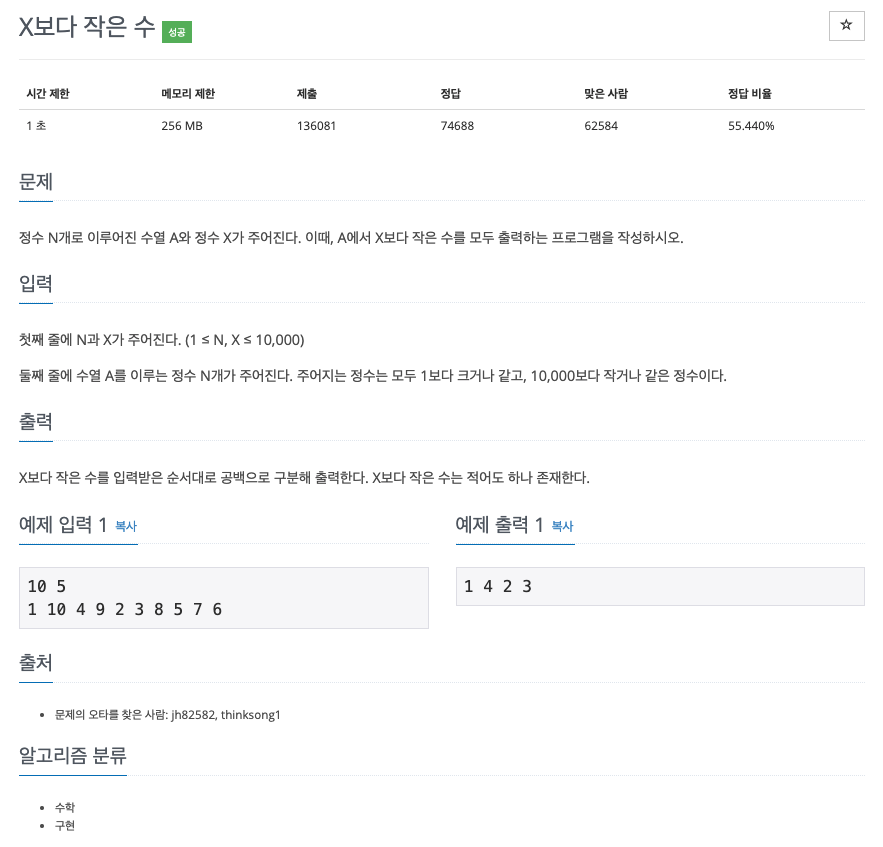
😢 N개의 수열을 받아서 X보다 작은지 판단하는 문제
😊 N, X을 먼저 입력받고, N만큼 loop, a는 X보다 작은지 판단하여 출력
| 백준 1000번: A+B(c++) (0) | 2021.09.27 |
|---|---|
| 백준 2752번: 세수정렬 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 백준 10804번: 카드 역배치 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.02 |
| 백준 2440번: 별 찍기 - 3 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.01 |
| 백준 2439번: 별 찍기 - 2 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
😢 iterate & swap!
😊 입력 받는 두 수(a, b)를 반복해서 입력해줘야하며,
a++, b--로 두 수를 증가 또는 감소시키는 것을 반복해야한다.
두 수가 같아졌을 경우 반복문을 빠져나오는 조건을 걸어줘야한다(a < b)
| 백준 2752번: 세수정렬 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
|---|---|
| 백준 10871번: X보다 작은 수 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 백준 2440번: 별 찍기 - 3 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.01 |
| 백준 2439번: 별 찍기 - 2 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
| 백준 2438번: 별 찍기 - 1 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
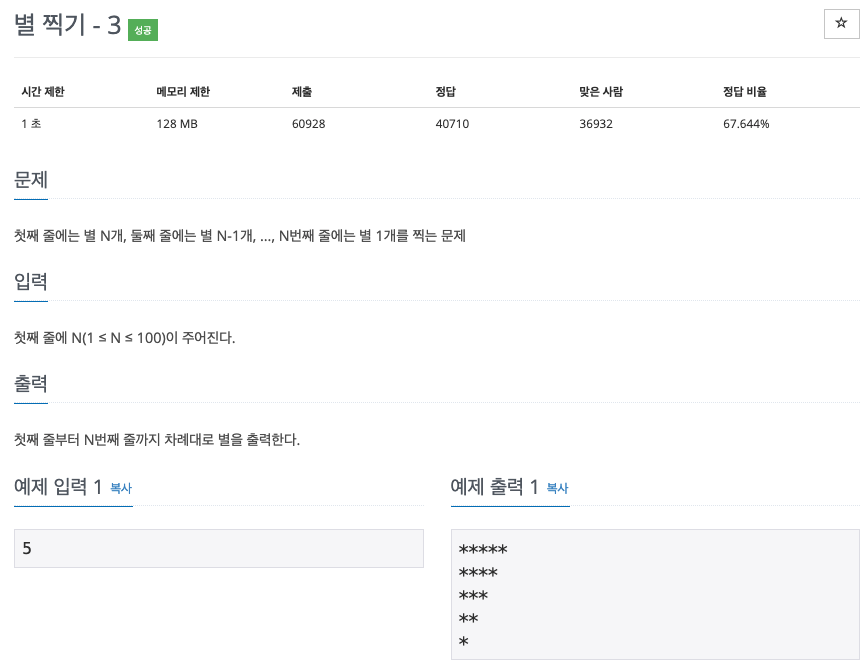
😢 단순 출력 문제
😊 row가 증가할 때마다 n-row만큼 줄어들도록 *을 출력하면 된다
row는 1개씩 증가하니
5를 입력받았을 경우
5-0, *****
5-1, ****
5-2, ***
5-3, **
5-4, *
| 백준 2752번: 세수정렬 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
|---|---|
| 백준 10871번: X보다 작은 수 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 백준 10804번: 카드 역배치 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.02 |
| 백준 2439번: 별 찍기 - 2 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
| 백준 2438번: 별 찍기 - 1 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.08.31 |

😢 단순 출력 문제(그래도 생각이 조금은 필요)
😊 *(별)은 row(행)의 수만큼 출력, 공백은 그 나머지 라는 생각을 통해 해결 가능
즉, 5를 입력받으면
1. 공백4개 별1개
2. 공백3개 별2개
3. 공백2개 별3개
4. 공백1개 별4개
5. 공백 0개 별5개
n을 입력받으면
for (int row = 0; row < n; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < n - row - 1; col++) cout << ' ';
for (int col = 0; col <= row; col++) cout << '*';
cout << '\n';
}
| 백준 2752번: 세수정렬 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
|---|---|
| 백준 10871번: X보다 작은 수 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 백준 10804번: 카드 역배치 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.02 |
| 백준 2440번: 별 찍기 - 3 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.01 |
| 백준 2438번: 별 찍기 - 1 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
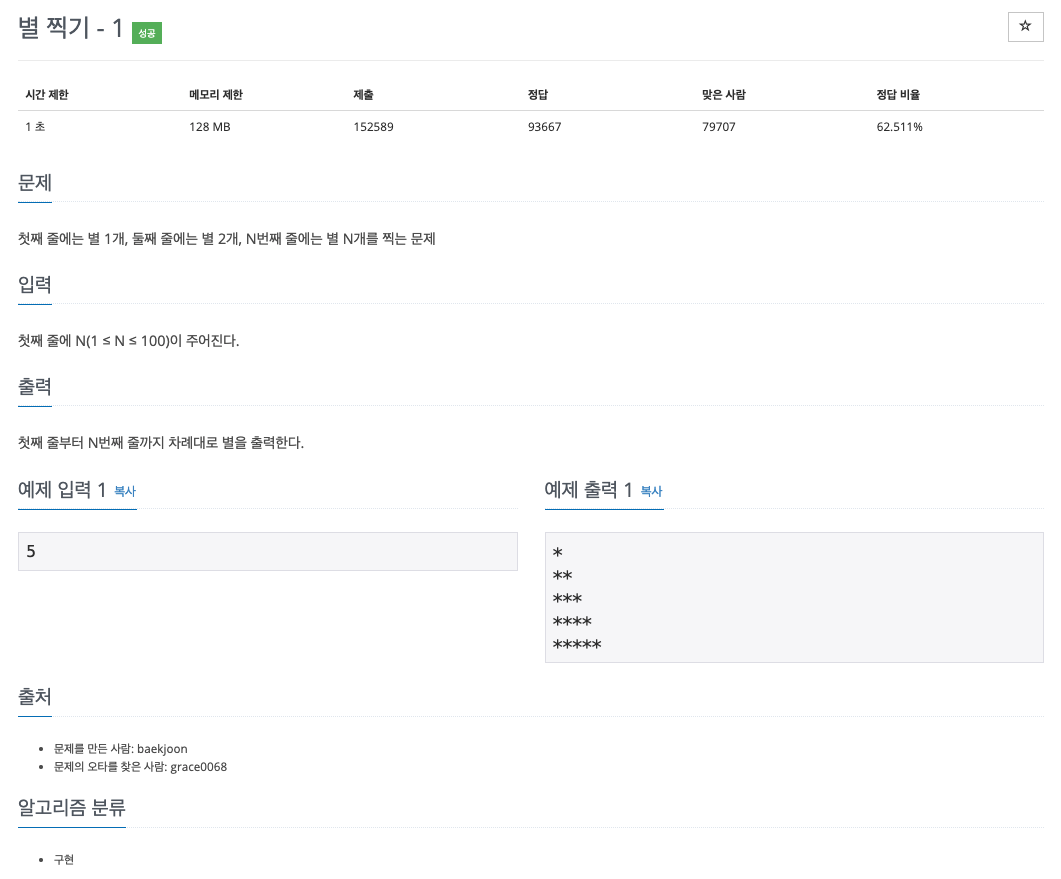
😢 단순 출력 문제
😊 1개부터 입력 받는 숫자만큼 1개씩 증가하는 별 출력
| 백준 2752번: 세수정렬 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
|---|---|
| 백준 10871번: X보다 작은 수 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 백준 10804번: 카드 역배치 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.02 |
| 백준 2440번: 별 찍기 - 3 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.09.01 |
| 백준 2439번: 별 찍기 - 2 c++(cpp) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
Code
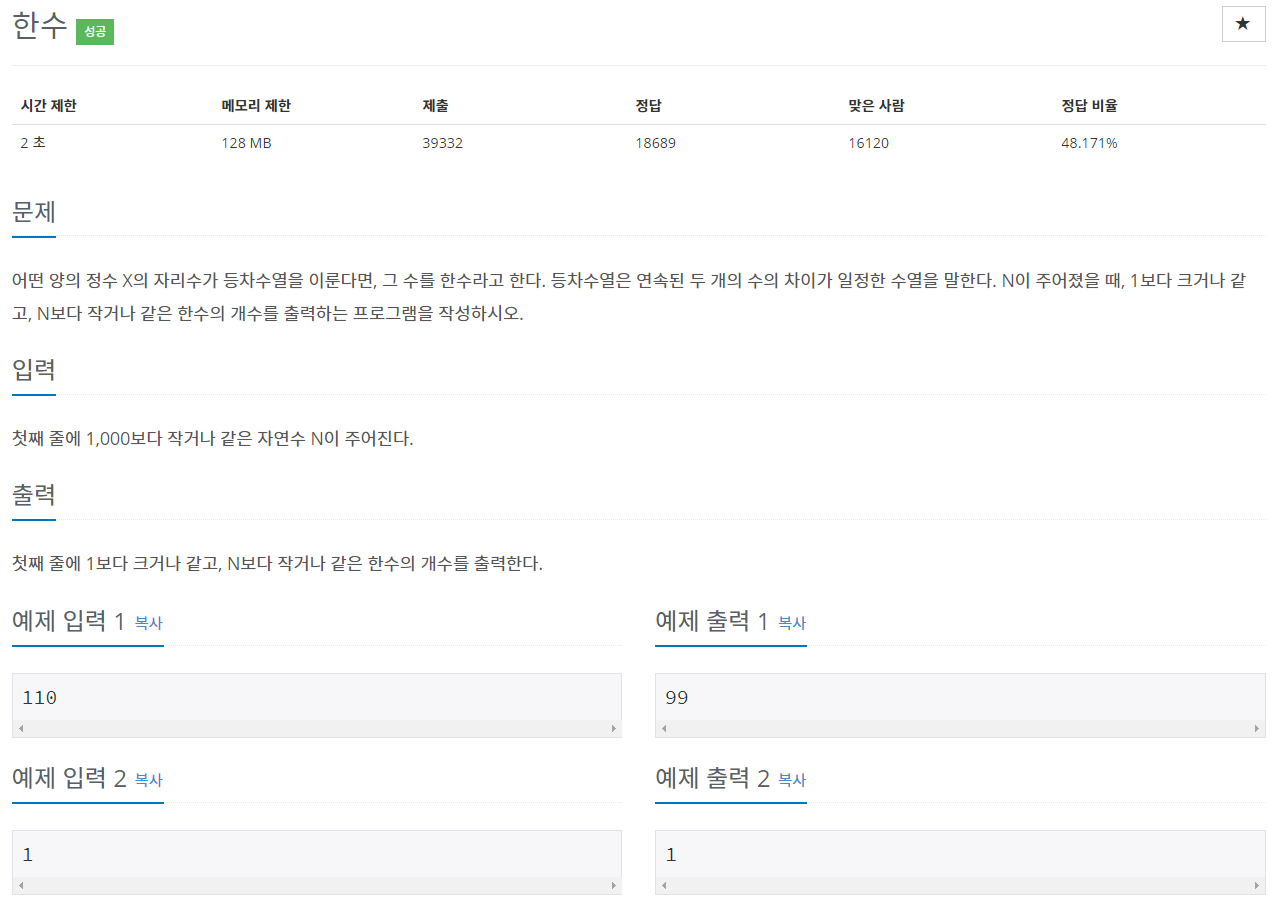
😢 '어떤 양의 정수 X의 자리수가 등차수열을 이룬다면'???? 지금 보면 별 것 아니지만, 처음 문제를 볼 때는 비슷한 문제를 풀어보지 못해서 그런지 이해하기 힘들었다. 문제 이해하는 것에 시간을 많이 보냈다.
😊 즉, 100미만의 수는 두 자릿수 또는 한 자릿수여서 등차수열을 확인할 수 없기 때문에 모두 '한수'가 된다.
그리고 세 자릿수부터 연속된 등차수열을 확인할 수 있다.
예를 들어, 우리에게 주어진 숫자 111을 백의 자리 1, 십의 자리1, 일의 자리1 하나씩 분리했다고 치자.
백의자리 1 - 십의자리 1 = 0 그리고 십의자리 1 - 일의자리 1 = 0 ( 1-1=0 === 1-1=0, true )
위처럼 연속된 두 개의 수 차이가 0으로 같다. 그렇다면 이건 한수이다.
그리고 1000은 '한수'가 아니다.
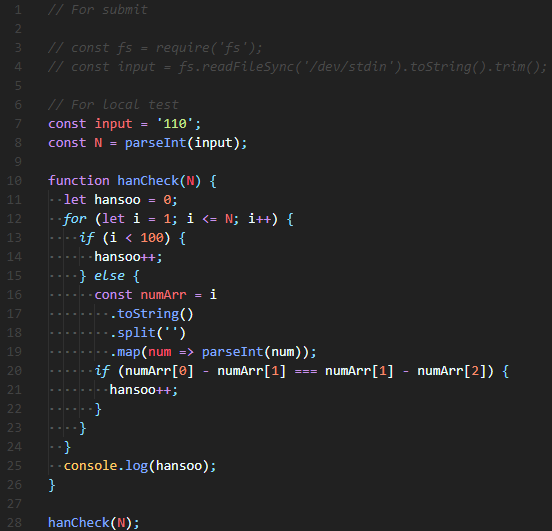
Solution 1) 기존 제출 코드
for loop안에서 100미만은 모두 한수로 count,
1000미만은 각 자릿수를 분리하여 Array에 넣고 각 자릿수 순서대로 빼주어 등차수열을 확인하였다.
만약 그 값이 한수라면 한수를 count해주었다. 그리고 1000은 한수가 아니기 때문에 else{ break; }으로 작성해주었다.
Solution 2) Other Solution
이 해결 방법은 다른 정답자의 답안을 참고하였다. 다른 방식으로 접근하였기 때문에 꼭 학습해두고 싶었다.
이 해결 방법에서는, classic for loop을 이용해서 function을 반복 호출하고 true값을 이용해 한수를 count해주었다.
특히, 세 자릿수가 들어오면 toString().split('').map을 이용해 Array로 만들어주고 값을 빼주어서 등차를 확인하였다.
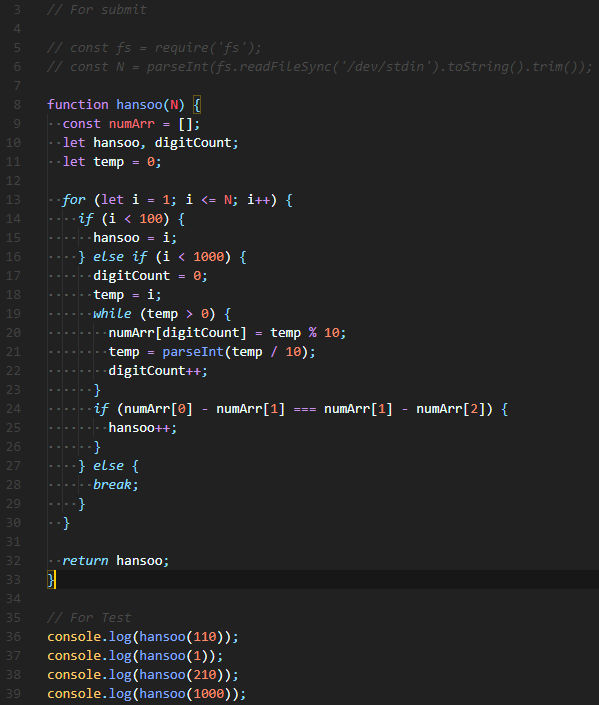
Solution 3) 최종 제출 코드
Solution 2)의 개선 버전이다. for loop을 2번 사용하지 않고, function 안에서 한 번만 for loop을 사용했다.
자릿수를 다루는 문제와 직면할 때는, while을 이용하여 자릿수를 분리하거나
문자열의 index를 이용하여 해결하곤 하는데, 항상 두 가지를 다 이용해보곤 한다.
프로그래밍은 한 가지 방법만 있지 않다는 게 가장 큰 매력인 것 같다.
Full Code
| // Hansoo(category - function) |
| // 1st Solution |
| // For submit |
| // const fs = require('fs'); |
| // const N = parseInt(fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim()); |
| function hansoo(N) { |
| const numArr = []; |
| let hansoo, digitCount; |
| let temp = 0; |
| for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) { |
| if (i < 100) { |
| hansoo = i; |
| } else if (i < 1000) { |
| digitCount = 0; |
| temp = i; |
| while (temp > 0) { |
| numArr[digitCount] = temp % 10; |
| temp = parseInt(temp / 10); |
| digitCount++; |
| } |
| if (numArr[0] - numArr[1] === numArr[1] - numArr[2]) { |
| hansoo++; |
| } |
| } else { |
| break; |
| } |
| } |
| return hansoo; |
| } |
| // For Test |
| console.log(hansoo(110)); |
| console.log(hansoo(1)); |
| console.log(hansoo(210)); |
| console.log(hansoo(1000)); |
| // For submit |
| // console.log(hansoo(N)); |
| // Other Solution(Solution 2) |
| // For submit |
| // const fs = require('fs'); |
| // const N = parseInt(fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim()); |
| // For Test |
| // const N = 110; |
| // function findHansoo(N) { |
| // if (N < 100) { |
| // return true; |
| // } else { |
| // const numArr = N.toString() |
| // .split('') |
| // .map(num => { |
| // return parseInt(num); |
| // }); |
| // if (numArr[0] - numArr[1] === numArr[1] - numArr[2]) { |
| // return true; |
| // } |
| // } |
| // return false; |
| // } |
| // let hansoo = 0; |
| // for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) { |
| // if (findHansoo(i)) { |
| // hansoo++; |
| // } |
| // } |
| // console.log(hansoo); |
| // 2nd Solution |
| // For submit |
| // const fs = require('fs'); |
| // const input = fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim(); |
| // For local test |
| // const input = '1000'; |
| // function hanCheck(num) { |
| // num = parseInt(num); |
| // let counter = 0; |
| // for (let i = 1; i <= num; i++) { |
| // if (i < 100) { |
| // counter++; |
| // } else if (i < 1000) { |
| // let temp = i; |
| // let numArr = []; |
| // let index = 0; |
| // while (temp > 0) { |
| // numArr[index] = temp % 10; |
| // temp = parseInt(temp / 10); |
| // index++; |
| // } |
| // if (numArr[0] - numArr[1] === numArr[1] - numArr[2]) { |
| // counter++; |
| // } |
| // } |
| // } |
| // console.log(counter); |
| // } |
| // hanCheck(input); |
| // 3rd Solution(최종 제출 코드) |
| // For submit |
| // const fs = require('fs'); |
| // const input = fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim(); |
| // For local test |
| // const input = '110'; |
| // const N = parseInt(input); |
| // function hanCheck(N) { |
| // let hansoo = 0; |
| // for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) { |
| // if (i < 100) { |
| // hansoo++; |
| // } else { |
| // const numArr = i |
| // .toString() |
| // .split('') |
| // .map(num => parseInt(num)); |
| // if (numArr[0] - numArr[1] === numArr[1] - numArr[2]) { |
| // hansoo++; |
| // } |
| // } |
| // } |
| // console.log(hansoo); |
| // } |
| // hanCheck(N); |
| 백준 11654번: 아스키 코드(ASCII Code) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.31 |
|---|---|
| 백준 1152번: 단어의 개수(The number of words) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.31 |
| Steps(#으로 계단 출력하기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.30 |
| Capitalize(단어의 첫 번째 알파벳을 대문자로 바꾸기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.30 |
| 백준 4673번: 셀프 넘버(Self Number) Node.js(JavaScript) [수정 및추가] (0) | 2019.12.29 |
Code
😢 무언가 원초적인 방법으로 풀었던 문제, 어떻게 풀어 나갈지에 대한 고민을 조금 했다.
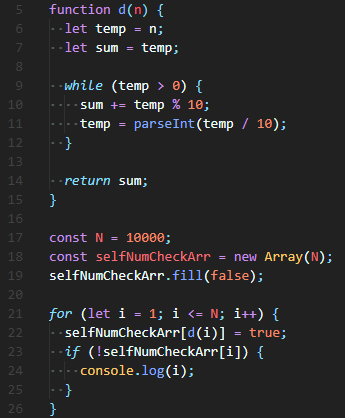
😊 기존 제출 Solution) array를 선언하고, 모든 index 값을 0으로 초기화해준 후 Self Number가 아니라면 해당 index에 1을 넣어주었다.
그리고 마지막에 for loop의 i를 이용해 array[i]의 값이 1이 아니라면(=Self Number라면) Self Number인 i를 출력하도록 했다.
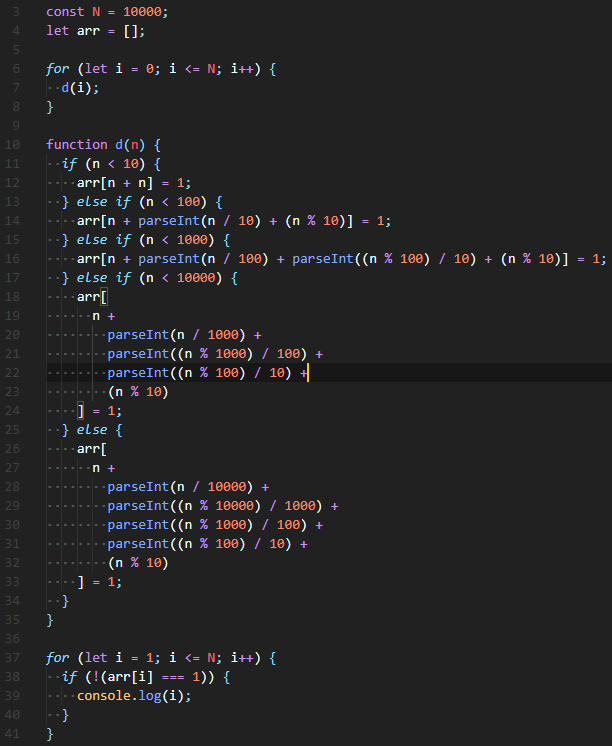
[추가] 최종 제출 Solution)
while loop 안에서 각 자릿수 나눠주기 + 나눠준 값 더하기를 진행하여 코드의 복잡도를 줄여줬다. 또한 시간도 더 빨라졌다.
그리고 배열 10000개 만큼 false로 채워주고, 셀프 넘버가 아니라면 true로 변경시켜주었다. 따라서 false로 남아있다면 그건 셀프 넘버다.
✔ 각 자릿수를 구하는 것은 매우 원초적인 방법으로 진행했다.
54321인 다섯 자리를 기준으로 설명하자면,
parseInt( 54321/10000 )(=5.4321)은 5
parseInt( (54321%10000) / 1000 )(=4.321)은 4
parseInt( (54321%1000) / 100 )(=3.21)은 3
parseInt( (54321%100) / 10 )(=2.1)은 2
54321 % 10 은 1
아래 Full Code에는 위의 자릿수 나누는 방식을, 다른 방법으로 접근한 Code가 있다.
✔ while loop을 이용한 자릿수 나누고, 바로 더하기
let temp = 나눌값;
let sum = temp;
while( 0 > temp){
sum += temp%10;
temp = parseInt(temp/10); }
또한, 다른 사람들이 푼 풀이가 매우 흥미로워서 그 방법들도 함께 연습했다. 세상에는 대단한 사람들이 참 많다.
Full Code (https://github.com/DasolPark/Dasol_JS_Algorithm/tree/master/Baekjoon)
| // Self Number |
| // 4th Solution |
| const n = 10000; |
| const isSelfNum = new Array(n + 1); |
| isSelfNum.fill(true); |
| function d(n) { |
| const N = n.toString().split(''); |
| return n + N.reduce((acc, num) => (acc += +num), 0); |
| } |
| for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) { |
| isSelfNum[d(i)] = false; |
| } |
| for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) { |
| if (isSelfNum[i]) { |
| console.log(i); |
| } |
| } |
| // 3rd Solution |
| // function d(n) { |
| // let temp = n; |
| // let sum = temp; |
| // while (temp > 0) { |
| // sum += temp % 10; |
| // temp = parseInt(temp / 10); |
| // } |
| // return sum; |
| // } |
| // const N = 10000; |
| // const selfNumCheckArr = new Array(N); |
| // selfNumCheckArr.fill(false); |
| // for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) { |
| // selfNumCheckArr[d(i)] = true; |
| // if (!selfNumCheckArr[i]) { |
| // console.log(i); |
| // } |
| // } |
| // 1st solution |
| // const N = 10000; |
| // let arr = []; |
| // for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { |
| // d(i); |
| // } |
| // function d(n) { |
| // if (n < 10) { |
| // arr[n + n] = 1; |
| // } else if (n < 100) { |
| // arr[n + parseInt(n / 10) + (n % 10)] = 1; |
| // } else if (n < 1000) { |
| // arr[n + parseInt(n / 100) + parseInt((n % 100) / 10) + (n % 10)] = 1; |
| // } else if (n < 10000) { |
| // arr[ |
| // n + |
| // parseInt(n / 1000) + |
| // parseInt((n % 1000) / 100) + |
| // parseInt((n % 100) / 10) + |
| // (n % 10) |
| // ] = 1; |
| // } else { |
| // arr[ |
| // n + |
| // parseInt(n / 10000) + |
| // parseInt((n % 10000) / 1000) + |
| // parseInt((n % 1000) / 100) + |
| // parseInt((n % 100) / 10) + |
| // (n % 10) |
| // ] = 1; |
| // } |
| // } |
| // for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) { |
| // if (!(arr[i] === 1)) { |
| // console.log(i); |
| // } |
| // } |
| // 2nd solution(string - array[index]) |
| // const N = 10000; |
| // const arr = []; |
| // for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { |
| // arr[i] = 0; |
| // } |
| // for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) { |
| // d(i); |
| // } |
| // function d(n) { |
| // const str = n.toString(); |
| // if (n < 10) { |
| // arr[n + n] = 1; |
| // } else if (n < 100) { |
| // arr[n + parseInt(str[0]) + parseInt(str[1])] = 1; |
| // } else if (n < 1000) { |
| // arr[n + parseInt(str[0]) + parseInt(str[1]) + parseInt(str[2])] = 1; |
| // } else if (n < 10000) { |
| // arr[ |
| // n + |
| // parseInt(str[0]) + |
| // parseInt(str[1]) + |
| // parseInt(str[2]) + |
| // parseInt(str[3]) |
| // ] = 1; |
| // } else { |
| // arr[ |
| // n + |
| // parseInt(str[0]) + |
| // parseInt(str[1]) + |
| // parseInt(str[2]) + |
| // parseInt(str[3]) + |
| // parseInt(str[4]) |
| // ]; |
| // } |
| // } |
| // for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) { |
| // if (arr[i] === 0) { |
| // console.log(i); |
| // } |
| // } |
| Steps(#으로 계단 출력하기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.30 |
|---|---|
| Capitalize(단어의 첫 번째 알파벳을 대문자로 바꾸기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.30 |
| Chunk(size만큼 sub array 잘라 넣기) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.29 |
| 백준 4344번: 평균은 넘겠지(It'll be above average) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.28 |
| Anagrams(철자 순서를 바꾼 말) Node.js(JavaScript) (0) | 2019.12.28 |